Discover the secrets to better email delivery and increased deliverability rates. Fix potential issues and enhance your email marketing reputation.
December 12, 2023
Navigating Email Deliverability: From Basics to Best Practices
Question
What should we do to improve email deliverability? And what are the biggest mistakes that quietly wreck sender reputation even when your emails themselves are fine?
Answer
You can improve deliverability, if you protect your sender reputation by keeping a high-quality, consented list, using double opt‑in, authenticating your domain (SPF/DKIM/DMARC), sending more relevant segmented content, and making opt‑out easy so people unsubscribe instead of marking you as spam.
Now, let’s dive a little deeper into email deliverability.
In this article, we will delve into the complexities of deliverability, exploring why even the most well-crafted emails can fail to reach their intended destinations and how to improve email deliverability. It’s important to note that the terms “email deliverability” and “email delivery rate, ” though frequently used interchangeably within email marketing, have distinct differences — let’s begin by taking a closer look at both of these concepts.
What is Email Delivery?
Email delivery, simply put, is the rate at which emails successfully arrive at the recipient’s mail server. The delivery rate (DR) can be calculated using the following formula:
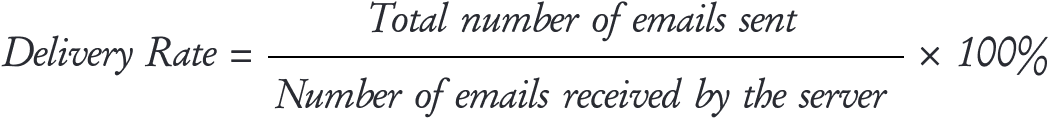
For example, if a company sends out emails to 100 clients and 55 emails land in the inbox, 25 in the promotions tab, 4 in the spam folder, and 16 bounce back, then the delivery rate would be:
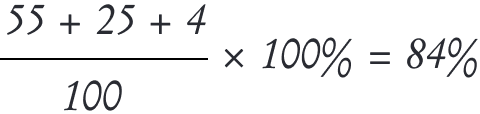
Today, Email Service Providers (ESPs) and platforms have largely automated the calculation of the delivery rate, integrating this metric into campaign reports for efficiency and insights. A good benchmark for the email delivery rate is 95% — anything less suggests there is a problem that needs to be identified and resolved.
What is Email Deliverability?
Email deliverability is the measure of an email campaign’s success in reaching subscribers’ inboxes. It is defined by the rate at which emails are not just sent but are successfully delivered to the intended recipient’s inbox without being filtered out as spam or junk. In essence, deliverability is the probability that an email sent will achieve its primary goal of being seen by the recipient.
Deliverability is difficult to calculate accurately because there is no reliable data on emails that land in spam, and email service providers do not provide this information.
Indirect indicators such as the open rate and click rate can hint at deliverability issues. For instance, if the delivery rate remains high at 99% but there is an unexpected dip in these engagement metrics, it could suggest that a larger portion of emails is being filtered into spam than usual.
Email Delivery Rate vs Email Deliverability
A simple way to distinguish between the two is to remember that deliverability consists of two components: the delivery rate and deliverability itself.
The email delivery rate measures all emails that landed in the client’s mailbox. This includes emails that end up in the spam folder, which the client is unlikely to read. The delivery rate is not used to assess the effectiveness of an email campaign — this metric helps to determine whether a company’s campaigns are reaching the client’s mailbox.
Email deliverability, indicates where the email ends up after being delivered: the inbox, the “Promotions” tab (for Gmail users), or the spam folder.
In essence, delivery merely confirms that an email has been received by the recipient’s email server, whereas deliverability dives deeper, gauging an email’s ability to pass through all the filters and barriers set up to protect users from unsolicited emails — this makes the email delivery rate a crucial benchmark in evaluating deliverability.
Why Does Email Deliverability Matter?
Email deliverability is vital to the success of your email marketing campaigns. It affects the visibility of your messages, shapes your sender reputation, and directly influences recipient engagement — let’s explore how deliverability impacts these crucial areas.
Direct Impact on Visibility
Deliverability determines your email content’s visibility. When emails fail to reach the inbox, the intended message remains unseen, and the potential for customer engagement and conversion is lost. This invisibility undermines the very purpose of email marketing and can render the resources dedicated to it obsolete.
Influence on Sender Reputation
The sender reputation is a score assigned to an email sender, used by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and Email Service Providers (ESPs) to determine the trustworthiness of an email source. This reputation influences whether an email will be delivered to the inbox, spam folder, or blocked entirely. ISPs and ESPs monitor how emails from a sender are received and treated by recipients. High rates of emails marked as spam or left unopened can damage this reputation, causing future communications to be directly filtered into spam folders or blocked. Sustained deliverability is key to maintaining a positive sender reputation.
Improved Engagement Metrics
Emails that successfully land in the inbox are more likely to be opened and engaged with. High deliverability rates correlate with higher open and click-through rates, leading to more effective campaigns. This engagement not only achieves immediate campaign goals but also helps increase email sender reputation, creating a reinforcing loop that supports future deliverability.
3 Factors That Affect Email Deliverability
While there are numerous issues that can impact email deliverability, they can all generally be grouped into three main buckets:
1. Sender Reputation and Email Authentication
In the same way that email deliverability affects sender reputation, the reverse is also true. Several key factors determine sender reputation, including:
- Email volume: Sudden spikes or irregular sending patterns can raise red flags. Consistent email volume is seen as more reliable.
- Bounce rates: A high number of bounced emails (emails that fail to be delivered) can negatively impact reputation, so keeping bounce rates low is crucial.
- Spam complaints: If recipients frequently mark emails as spam, this is a strong negative signal that lowers sender reputation.
- Engagement rates: Positive interactions with emails, such as opens, clicks, and forwards, indicate good sender reputation.
Coupled with this is email authentication, involving protocols like Sender Policy Framework (SPF), DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM), and Domain-Based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) – more on these below. Together, the protocols work to verify the sender's identity and contribute to a positive reputation, which is essential for bypassing spam filters.
2. Legal Compliance
Compliance with laws like the CAN-SPAM Act in the U.S. is crucial for legal reasons and for maintaining a good sender reputation, which in turn affects deliverability. The CAN-SPAM Act sets several requirements for commercial emails — this includes:
- Using honest headers where the “From, ” “To, ” “Reply-To, ” and routing information accurately identify the person or business who initiated the email.
- Using subject lines that reflect the content of the email.
- If the email is an advertisement, this should be clearly disclosed — for instance, using language that unmistakably indicates its promotional nature. An example of a subject line that does this could be: "Summer Sale: 40% Off Our Entire Collection."
- Including a valid physical postal address for the sender.
- Providing a clear and easy method for recipients to unsubscribe from future emails, and promptly honoring these requests.
3. Email Content Quality
Good quality email content is relevant and tailored to the audience’s interests, which increases the likelihood of engagement, such as opens and clicks. The clarity and conciseness of the email content are also crucial: clear and well-written emails are more effective and less likely to be disregarded by the recipient. Subject lines are the first point of contact with the recipient and should be engaging yet honest, reflecting the true content of the email. It’s also important to avoid triggers commonly associated with spam, such as overuse of capital letters, excessive punctuation, and overly promotional language like “Buy now!” or “Free offer!” — these can prompt spam filters to flag the email.
In addition, an email with too many images or images that are too large can not only affect loading times but also raise flags with spam filters.
How to Improve Your Email Deliverability
Improve the Quality of Your Subscriber Base
To improve email deliverability, it’s essential to maintain a high-quality subscriber base. This involves:
- Removing invalid addresses that contain errors or consistently fail to receive emails. Manually checking the validity of each address is time-consuming, so many businesses use email validators. These services can automatically remove nonexistent addresses, duplicates, and improperly formatted addresses from the database. They can also provide reports or prepare lists for SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) or FTP (File Transfer Protocol) servers for distribution. The cost of such services generally depends on the number of addresses in your database, with larger databases often benefiting from lower costs per address verification.
- Incorporating a format validation step during email registration can prevent users from entering incorrect addresses.

For example, this brand rejects all customer email addresses if they lack an “@” symbol
- Routinely clean your database to remove email addresses that are no longer receiving emails. Advanced ESP platforms can automate this process by identifying and removing such addresses. Platforms like Maestra categorize these addresses into a global list and automatically exclude them from future email campaigns.
- Avoid purchasing or scraping email lists from the internet for your campaigns at all costs — these can be fraught with invalid or outdated addresses. Using such lists can not only harm your domain’s reputation but also increase the likelihood of degrading the overall effectiveness of your email deliverability.
Implement Double Opt-In
Double opt-in, or DOI, is a two-step subscription confirmation process. To subscribe to a newsletter, a customer must not only enter their email on a website form, but also confirm their subscription via a button in a confirmation email. This process ensures the email address exists, can receive emails without issues, and that the owner has explicitly expressed their desire to receive newsletters. It protects against adding nonexistent addresses, addresses with typos, and spam complaints — for instance, when an email address is entered by someone other than the owner.
DOI also safeguards against spam traps set by email providers, which are special email addresses owned by the provider. Sending messages to these addresses can result in being blocklisted by email servers.
Configure Email Authentication Protocols
Setting up email authentication protocols such as SPF, DKIM, and DMARC is essential for protecting against email fraud and improving deliverability.
- SPF specifies which servers and IP addresses are authorized to send emails for your domain, thus confirming the email’s origin.
- DKIM provides an additional layer of verification, akin to a digital signature, ensuring the email has indeed been sent from the claimed domain.
- DMARC allows you to specify how to handle emails that fail SPF and DKIM checks — whether to reject them, mark them as spam, or deliver them to the inbox. Without DMARC, these decisions are left to the receiving email server. DMARC also compels the email server to send reports to the domain administrator about the sent emails and how these were treated by the email service.
Collectively, these protocols play a vital role in safeguarding your recipients from phishing attempts and enhancing the trustworthiness of your emails.
Segment Your Recipients
Dividing your audience into distinct groups based on specific criteria enables you to tailor your communications to better meet the needs and preferences of each segment. The more fine-tuned these segments are, the more personalized and impactful each email becomes, leading to higher engagement, lower unsubscribe rates, and improved deliverability.
For instance, you can create segments based on factors like purchase history, style preferences, age, or a combination of multiple features for ultra-precise targeting. This will allow you to compose tailored emails that customers find relevant and even look forward to.
Create a Smooth Opt-Out Process
Having an easy opt-out process is crucial in maintaining a healthy and relevant email list — it ensures that those who remain are genuinely interested in your content. This approach not only keeps your list up-to-date but also enhances your overall campaign performance by focusing on an engaged audience, leading to higher open and click-through rates and reduced bounce rates.
Avoid any temptation to make the opt-out process obscure. A straightforward unsubscribe option — such as a clear link or button at the bottom of your emails — respects the recipient’s preferences and enhances the user experience. Making it difficult to unsubscribe can backfire, as frustrated recipients might resort to marking your emails as spam. Users appreciate a hassle-free way to opt out, which in turn can leave a positive impression of your brand’s respect for their choices.
Implementing a one-click unsubscribe process is optimal. However, providing an optional feedback form for users who choose to unsubscribe can offer valuable insights. Understanding why subscribers choose to leave can help you refine your email strategy and improve future content.
Feedback forms can give you a better understanding of why customers unsubscribe from notifications and what you can do to improve their experience
Email Deliverability: Recap
Email deliverability is a crucial aspect of email marketing that should not be overlooked. It’s not just about sending out messages, but ensuring they reach and engage the intended audience. The success of an email campaign hinges significantly on this key factor.
To achieve this, it’s essential to maintain a clean and engaged email list, craft relevant and engaging content, adhere to legal standards, and implement robust email authentication protocols. These steps are fundamental in ensuring that emails not only reach the server but also make their way to the recipient’s inbox.
A strong delivery rate is a key indicator in email marketing, reflecting whether your emails are successfully reaching the recipients and thereby impacting the overall effectiveness of your campaign. Moreover, understanding the nuances between the email delivery rate and deliverability is essential. While delivery focuses on whether an email reaches the server, deliverability is concerned with whether it makes it to the inbox.
Improving email deliverability is a continuous process. It involves adapting to evolving email practices, understanding recipient behavior, and leveraging technological advancements. When executed well, these efforts lead to improved campaign performance, stronger audience relationships, and a higher return on investment in email marketing.


